A contactor is an electrically controlled switch used to switch electrical circuits, similar to a relay except that it has a higher rated current. It can be said that the contactor is an intermediate part to switch off the power supply to the load (electric motor, water pump or power supply …), manually (via the button system) or automatically.
Because the contactor is a very basic device, used a lot in the electrical control system, so it occupies a significant part of the overall electrical system. Therefore, it is necessary to calculate to choose the appropriate type both in terms of size and features of use. Usually, manufacturers already support the selection of contactors with the right motor capacity right on their product catalogs. However, in some cases the design requires, or there are separate requirements, we still have to calculate to choose accordingly.
I. Things to Consider When Choosing a Contactor
1. Engine catalog
There are many types of downloads for contactor. Each type will have different usage characteristics for which the device is designed. These types of loads will be defined according to the IEC standard. Currently motors used in industrial applications fall under the category of AC-3 loads.
| Load symbol |
Engine Application |
| AC-1 | Application for non-inductive, light induction motor loads such as heaters |
| AC-2 | Application for load asynchronous slip ring motor, motor start brake, click release. |
| AC-3 | Shock cage motor loading application: starting, stopping the engine while running. |
| AC-4 | Shock cage motor loading applications: Start-up, brake, reverse |
2. Starting current of the motor
Compared to the running current of the motor, during starting; the starting current of the motor will be much higher. Therefore, when choosing contactor, it is necessary to ensure that the device can withstand this large current. Accordingly, the rated current of the device will be specified for the AC load – 3. Because the AC load – 3 will be lower than the AC load – 1.
3. Supply voltage
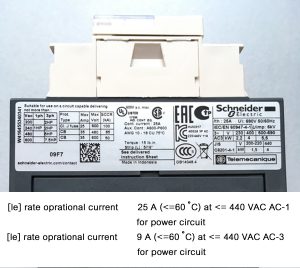
Usually the power source commonly used in industrial parks is a three-phase 400V power source. But there are also a few places that will use 110V voltage sources. In particular, in heavy industrial zones in Japan can use power up to 690V. Depending on the voltage used, the selected must also ensure the appropriate factor.

As shown above, the contactor can withstand 7A current for 440VAC, but with 550VAC voltage it can only withstand 6A current.
II. Steps to select the right contactor for the motor application
Step 1: Look carefully at the parameter table printed on the motor
There are 3 electrical properties that you need to know when choosing a contactor. Those are voltage, current and power. For example picture:
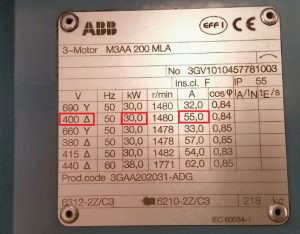
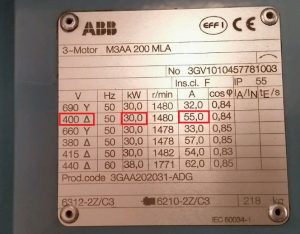
As shown in the table of ABB motor parameters above, if the voltage used is 400V, the motor must have a capacity of 30kW and the current required to ensure operation must be 55A.
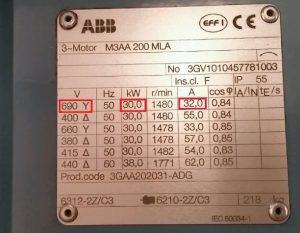
But if the voltage used is 690V, the motor required is still 30kW but the current that needs to be selected must be 32A.
Step 2: Refer to the manufacturer’s contactor technical documentation for suitable selection for the type of load
You can only select contactor when you find the correct manufacturer’s catalogs along with the technical data sheet. Thus, making selection decisions will be much more effective.
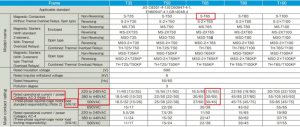
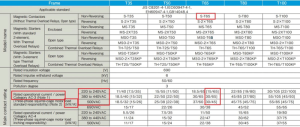
Product specification sheet Contactor S-T65 Mitsubishi
Step 3: Make contactor selection
Once you have consulted the catalog and technical documents provided by the manufacturer, you can make the final choice. For example: with a voltage of 400V and an operating frequency of 50Hz; If the motor works at 30kW and 55A current, you can consider Mitsubishi’s S-T65 contactor line. This is a magnetic contactor line with the ability to withstand currents up to 65A. This level of amperage will certainly be much higher than that of a motor operating at 55A.